-
Generating CuII-Oxyl/CuIII-Oxo Species from CuI- α-Ketocarboxylate Complexes and O2: In silico studies on ligand effects and C-H-activation reactivity
S.M. Huber, M.Z. Ertem, F. Aquilante, L. Gagliardi, W.B. Tolman and C.J. Cramer
Chemistry - A European Journal, 15 (19) (2009), p4886-4895


DOI:10.1002/chem.200802338 | unige:3742 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF
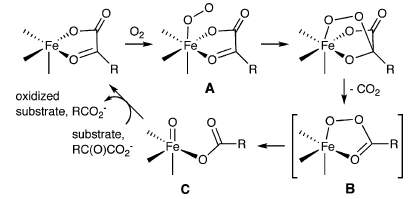
Theoretically speaking: The mechanistic details associated with the generation and reaction of [CuO]+ species from CuI-α-ketocarboxylate complexes, especially with respect to modifications of the ligand supporting the copper center, were investigated (see scheme). Theoretical models were used to characterize the electronic structures of different [CuO]+ species and their reactivity in CH activation and O-atom transfer reactions.